Fractal Space
Fractal Space is a scientific discipline which studies the fractal nature of energy distribution in the universe. According to this theoretical science, there are several layers or d-branes to the universe. They are as follows:
- Normal Space: Normal space, or N-Space, is the universe in which we exist. It follows the fundamental rules of physics and must adhere to the rules of conservation of energy.
- Subspace: subspace, or S-Space, is a layer of space immediately beneath Normal space. It is characterized by the bending of several fundamental rules of conventional physics, including the absolute limits of velocity. It is Subspace that allows the utilization of Warp drive.
- Fractal Space: Fractal space, or F-Space, was considered to be nothing more than a mathematical theory until 2408. The conceptualization of Fractal Space, however dates back to 1890, and was first put forward by Guiseppe Peano. The exact properties of F-Space are unmeasured, although reinforced wave motion has been observed in the Tch'Kairn fractal spacial communications signal.
- Phase Space: Phase space, or P-Space, is comprised of an infintie number of dimensional membranses which are only separated from the other layers of space due to quantum resonance. it is possible to shift ones quantum resonance into another layer of P-Space, through the use of a Phase variant modulator.
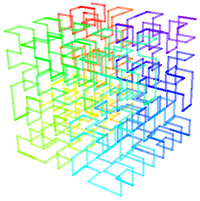
Fractal space is best visually described by the Hilbert curve (also known as a Hilbert space-filling curve), which is a Geometrically continuous fractal space-filling curve first described by the German mathematician David Hilbert in 1891, as a variant of the space-filling curves discovered by Giuseppe Peano in 1890.
Because it is space-filling, its Hausdorff dimension is 2 (precisely, its image is the unit square, whose dimension is of course 2 in any definition of dimension; its graph is a compact set homeomorphic to the closed unit interval, with Hausdorff dimension 2).
H_n is the nth approximation to the limiting curve. The Euclidean length of H_n is 2^n - {1 \over 2^n} , i.e., it grows exponentially with n, while at the same time always being bounded by a square with a finite area.
For multidimensional databases, Hilbert order has been proposed to be used instead of Z order because it has better locality-preserving behavior.